最近更新于 2024-05-05 14:18
代码
顺序存储实现
stack.h
#ifndef STACK_H
#define STACK_H
#define STACK_MAX 1024
typedef struct stack
{
void *data[STACK_MAX];
int size;
} stack;
/**
* @brief 初始化栈
* @return 返回栈结构
*/
stack *init_stack();
/**
* @brief 入栈
* @param s 栈结构
* @param data 数据
*/
void push_stack(stack *s, void *data);
/**
* @brief 出栈
* @param s 栈结构
*/
void pop_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈顶数据
* @param s 栈结构
* @return 返回栈顶数据地址
*/
void *top_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈的实际大小
* @param s 栈结构
* @return 返回大小数值
*/
int get_size_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈是否为空
* @param s 站栈结构
* @return 1 栈为空,0 栈不为空
*/
int empty_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 销毁栈
* @param s 栈结构
*
*/
void destroy_stack(stack *s);
#endifstack.c
#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
stack *init_stack()
{
stack *s = (stack *)malloc(sizeof(stack));
memset(s->data, 0, sizeof(void *) * STACK_MAX);
s->size = 0;
return s;
}
void push_stack(stack *s, void *data)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("push_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return;
}
if (data == NULL)
{
printf("push_stack: 传入的数据为空!");
return;
}
if (s->size > STACK_MAX)
{
printf("push_stack: 栈已存满!");
return;
}
s->data[s->size] = data;
++s->size;
}
void pop_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("pop_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
printf("pop_stack: 栈为空!");
return;
}
s->data[s->size - 1] = NULL;
--s->size;
}
void *top_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("top_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return NULL;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
printf("top_stack: 栈为空!");
return NULL;
}
return s->data[s->size - 1];
}
int get_size_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("get_size_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return 0;
}
return s->size;
}
int empty_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("empty_stack: 传入的栈结构为空");
return 1;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void destroy_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("destroy_stack: 传入的栈结构为空");
return;
}
free(s);
s = NULL;
}链式存储实现
stack.h
#ifndef STACK_H
#define STACK_H
typedef struct node
{
void *data;
struct node *next;
} node;
typedef struct stack
{
struct node *head;
int size;
} stack;
/**
* @brief 初始化栈
* @return 返回栈结构
*/
stack *init_stack();
/**
* @brief 入栈
* @param s 栈结构
* @param data 数据
*/
void push_stack(stack *s, void *data);
/**
* @brief 出栈
* @param s 栈结构
*/
void pop_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈顶数据
* @param s 栈结构
* @return 返回栈顶数据地址
*/
void *top_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈的实际大小
* @param s 栈结构
* @return 返回大小数值
*/
int get_size_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 获取栈是否为空
* @param s 站栈结构
* @return 1 栈为空,0 栈不为空
*/
int empty_stack(stack *s);
/**
* @brief 销毁栈
* @param s 栈结构
*
*/
void destroy_stack(stack *s);
#endifstack.c
#include "stack.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
stack *init_stack()
{
node *new_node = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
new_node->data = NULL;
new_node->next = NULL;
stack *s = (stack *)malloc(sizeof(stack));
s->head = new_node;
s->size = 0;
return s;
}
void push_stack(stack *s, void *data)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("push_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return;
}
node *new_node = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = s->head->next;
s->head->next = new_node;
++s->size;
}
void pop_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("pop_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
printf("pop_stack: 栈为空!");
return;
}
node *tmp = s->head->next;
s->head->next = s->head->next->next;
--s->size;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}
void *top_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("top_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return NULL;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
printf("top_stack: 栈为空!");
return NULL;
}
return s->head->next->data;
}
int get_size_stack(stack *s)
{
return s->size;
}
int empty_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("empty_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return 1;
}
if (s->size == 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void destroy_stack(stack *s)
{
if (s == NULL)
{
printf("destroy_stack: 传入的栈结构为空!");
return;
}
while (s->head)
{
node *tmp = s->head;
s->head = s->head->next;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}
free(s);
s = NULL;
}测试代码
stack_demo.c
#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct student
{
char name[12];
int age;
} student;
int main()
{
stack *s = init_stack();
printf("1.栈是否为空:%d\n", empty_stack(s));
student s1 = {"Tom", 20};
student s2 = {"Aron", 19};
student s3 = {"Jack", 21};
student s4 = {"Jery", 20};
push_stack(s, &s1);
push_stack(s, &s2);
push_stack(s, &s3);
push_stack(s, &s4);
printf("2.栈是否为空:%d\n", empty_stack(s));
printf("3.栈的大小为: %d\n", get_size_stack(s));
while (get_size_stack(s))
{
student *ss = top_stack(s);
printf("出栈获取数据为: %s %d\n", ss->name, ss->age);
pop_stack(s);
}
printf("8.栈是否为空:%d\n", empty_stack(s));
destroy_stack(s);
}运行效果
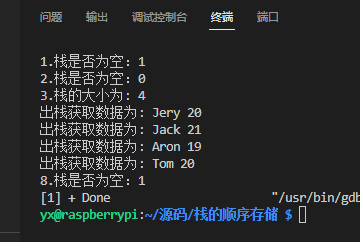
C 语言栈的简单实现