最近更新于 2024-05-05 12:30
1 环境
Arduino UNO
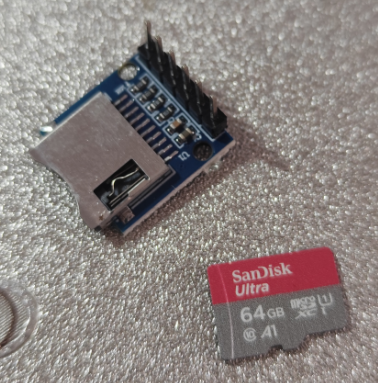
SD 卡模块
Arduino IDE 2.2.1
SdFat 2.2.3:https://github.com/adafruit/SdFat
这个库支持 FAT16/FAT32/exFAT(Arduino 官方的 SD 库不支持 exFAT),FAT16 比较古老了,应该是在内存卡普遍几百兆容量的时候,容量小于 2G 的卡中使用,FAT32 支持最大 128GB,单文件最大4G,Windows 11 上容量大于 32G 的储存设备就不让格式化为 FAT32 了,一般使用范围大致就在 2~32 之间的,大于 32G 的基本就是用 exFAT 了,现在的内存卡还没有能达到 exFAT 文件系统上限的,单个文件最大都支持 16EB(1EB=10^9GB)。我这里就用一张以前买的 64G 的闪迪内存卡测试。
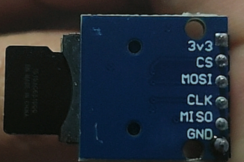
接线(SPI)
\begin{array}{l l}
Arduino & SD卡模块 \\
\hline
GND & GND \\
3v3 & 3.3V \\
MOSI & 11 \\
MISO & 12 \\
CLK & 13 \\
CS & 4 \\
\end{array}注:
-
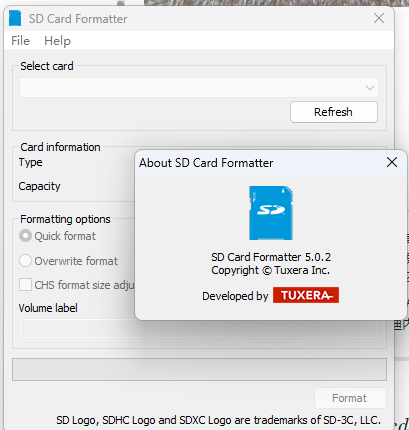
格式化内存卡建议使用 SD 卡协会的软件:https://www.sdcard.org/downloads/formatter/sd-memory-card-formatter-for-windows-download/
我用 Windows 的格式化,内存卡始终无法读取有效的 MBR,用标准的格式化软件就没问题。

-
中文文件名读取出来会显示问号,但是好过 SD 库,至少不会有中文名就崩溃,保证还能用。
2 SD 卡信息显示
#include "SdFat.h"
#include "sdios.h"
const int8_t DISABLE_CS_PIN = -1; // 禁止其它 CS 引脚,没有其它 SPI 设备置为 -1 就行
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = 4; // 定义使用的 CS 引脚
// 接口类型选择
////////////////////
#define ENABLE_DEDICATED_SPI 1 // 这个 SD 卡模块是 SPI 通信的,这里没有使用其它 SPI 设备就是专用的
// SPI 时钟频率设置
// 在面包板接线测试等环境中建议设置 4
// 线路较长,线路的电容电感等都可能对高频信号传输产生影响,导致数据不完整,采用较低的速度可以更为稳定
// 在实际部署的环境中,SD 卡连接线路要尽可能的短,电源供电等也要保证稳定,可以尝试不超过 50 的频率以获得高速读写
// 可以从较大的数值开始尝试,遇到报错就减小
const uint8_t sd_sck = 4; // MHz
#if HAS_SDIO_CLASS // SDIO 接口
#define SD_CONFIG SdioConfig(FIFO_SDIO)
#elif ENABLE_DEDICATED_SPI
#define SD_CONFIG SdSpiConfig(SD_CS_PIN, DEDICATED_SPI, SD_SCK_MHZ(sd_sck)) // 专用 SPI 接口
#else
#define SD_CONFIG SdSpiConfig(SD_CS_PIN, SHARED_SPI, SD_SCK_MHZ(sd_sck)) // 共享的 SPI 接口
#endif
// 存储内存卡信息
SdFs sd;
cid_t cid;
csd_t csd;
scr_t scr;
uint8_t cmd6Data[64];
uint32_t eraseSize;
uint32_t ocr;
static ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial);
/**
* @brief 显示制造商信息
*/
void cidDmp()
{
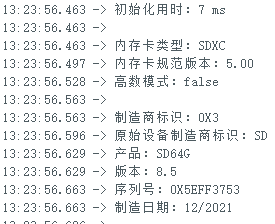
cout << F("\n制造商标识:");
cout << uppercase << showbase << hex << int(cid.mid) << dec << endl;
cout << F("原始设备制造商标识:") << cid.oid[0] << cid.oid[1] << endl;
cout << F("产品:");
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << cid.pnm[i];
}
cout << F("\n版本:") << cid.prvN() << '.' << cid.prvM() << endl;
cout << F("序列号:") << hex << cid.psn() << dec << endl;
cout << F("制造日期:");
cout << cid.mdtMonth() << '/' << cid.mdtYear() << endl;
cout << endl;
}
/**
* @brief 清除串口缓冲区中的数据
*/
void clearSerialInput()
{
uint32_t m = micros();
do
{
if (Serial.read() >= 0)
{
m = micros();
}
} while (micros() - m < 10000);
}
/**
* @brief 显示卡的容量和擦除信息
*/
void csdDmp()
{
eraseSize = csd.eraseSize();
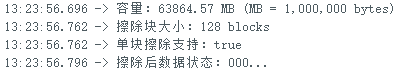
cout << F("容量:") << 0.000512 * csd.capacity();
cout << F(" MB (MB = 1,000,000 bytes)\n");
cout << F("擦除块大小:") << int(eraseSize) << F(" blocks\n");
cout << F("单块擦除支持:");
if (csd.eraseSingleBlock())
{
cout << F("true\n");
}
else
{
cout << F("false\n");
}
cout << F("擦除后数据状态:");
if (scr.dataAfterErase())
{
cout << F("111...\n");
}
else
{
cout << F("000...\n");
}
}
/**
* @brief 显示错误代码和错误数据
*/
void errorPrint()
{
if (sd.sdErrorCode())
{
cout << F("SD 错误代码:") << hex << showbase;
printSdErrorSymbol(&Serial, sd.sdErrorCode());
cout << F(" = ") << int(sd.sdErrorCode()) << endl;
cout << F("SD 错误数据:") << int(sd.sdErrorData()) << dec << endl;
}
}
/**
* @brief 显示主引导记录(MBR)
*/
bool mbrDmp()
{
MbrSector_t mbr; // 用于存储 MBR 数据
bool valid = true; // MBR 有效性记录
if (!sd.card()->readSector(0, (uint8_t *)&mbr)) // 读取扇区 0 的数据
{
cout << F("\n读取 MBR 失败。\n");
errorPrint();
return false;
}
cout << F("\nSD 分区表:\n");
cout << F("分区编号,引导标志,起始柱面/磁头/扇区(CHS),分区类型,结束 CHS 值,相对扇区数,总扇区数\n");
for (uint8_t ip = 1; ip < 5; ip++) // 遍历分区表中的 4 个分区
{
MbrPart_t *pt = &mbr.part[ip - 1];
if ((pt->boot != 0 && pt->boot != 0X80) || getLe32(pt->relativeSectors) > csd.capacity())
{
valid = false;
}
cout << int(ip) << ',' << uppercase << showbase << hex;
cout << int(pt->boot) << ',';
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << int(pt->beginCHS[i]) << ',';
}
cout << int(pt->type) << ',';
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << int(pt->endCHS[i]) << ',';
}
cout << dec << getLe32(pt->relativeSectors) << ',';
cout << getLe32(pt->totalSectors) << endl;
}
if (!valid)
{
cout << F("\nMBR无效,假定为超级软盘格式。\n");
}
return true;
}
void dmpVol()
{
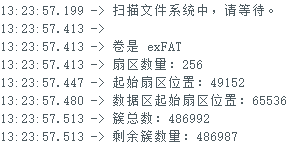
cout << F("\n扫描文件系统中,请等待。\n");
int32_t freeClusterCount = sd.freeClusterCount(); // 获取剩余簇数量
if (sd.fatType() <= 32)
{
cout << F("\n卷是 FAT") << int(sd.fatType()) << endl;
} else {
cout << F("\n卷是 exFAT\n");
}
cout << F("扇区数量:") << sd.sectorsPerCluster() << endl;
cout << F("起始扇区位置:") << sd.fatStartSector() << endl;
cout << F("数据区起始扇区位置:") << sd.dataStartSector() << endl;
cout << F("簇总数:") << sd.clusterCount() << endl;
cout << F("剩余簇数量:");
if (freeClusterCount >= 0)
{
cout << freeClusterCount << endl;
}
else
{
cout << F("失败!\n");
errorPrint();
}
}
/**
* @brief 显示内存卡类型
*/
void printCardType()
{
cout << F("\n内存卡类型:");
switch (sd.card()->type())
{
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
{
cout << F("SD1\n"); // 1MB~2GB
break;
}
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
{
cout << F("SD2\n"); // ~4GB
break;
}
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
{
if (csd.capacity() < 70000000)
{
cout << F("SDHC\n"); // 4~32GB
}
else
{
cout << F("SDXC\n"); // 32G~2TB
}
break;
}
default:
{
cout << F("未知\n");
}
}
}
/**
* 显示配置信息
*/
void printConfig(SdSpiConfig config)
{
if (DISABLE_CS_PIN < 0)
{
cout << F(
"\n假设 SD 卡是唯一的 SPI 设备\n"
"编辑DISABLE_CS_PIN以禁用其它SPI设备。\n");
}
else
{
cout << F("\n禁用引脚上的SPI设备:");
cout << int(DISABLE_CS_PIN) << endl;
pinMode(DISABLE_CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(DISABLE_CS_PIN, HIGH);
}
cout << F("\n假设 SD 卡的 CS 引脚是:") << int(config.csPin);
cout << F("\n编辑SD_CS_PIN修改片选引脚。\n");
}
void printConfig(SdioConfig config)
{
(void)config;
cout << F("假设正在使用 SDIO 接口。\n");
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) // 等待 USB 串口
{
yield();
}
cout << F("SdFat 版本:") << SD_FAT_VERSION_STR << endl;
printConfig(SD_CONFIG);
}
void loop()
{
clearSerialInput();
cout << F("\n输入任意字符继续\n");
while (!Serial.available())
{
yield();
}
uint32_t t = millis();
if (!sd.cardBegin(SD_CONFIG))
{
cout << F(
"\nSD 初始化失败。\n"
"不要重新格式化内存卡!\n"
"内存卡是否正确插入?\n"
"是否存在接线错误或者接触不良的问题?\n");
if (isSpi(SD_CONFIG))
{
cout << F(
"SD_CS_PIN 是否设置了正确的值?\n"
"是否需要禁用其它 SPI 设备?\n");
}
errorPrint();
return;
}
t = millis() - t;
cout << F("初始化用时:") << dec << t << " ms" << endl;
if (!sd.card()->readCID(&cid) || !sd.card()->readCSD(&csd) || !sd.card()->readOCR(&ocr) || !sd.card()->readSCR(&scr))
{
cout << F("读取信息失败!\n");
errorPrint();
return;
}
printCardType();
cout << F("内存卡规范版本:") << 0.01 * scr.sdSpecVer() << endl;
cout << F("高数模式:");
if (scr.sdSpecVer() && sd.card()->cardCMD6(0X00FFFFFF, cmd6Data) && (2 & cmd6Data[13]))
{
cout << F("true\n");
} else {
cout << F("false\n");
}
cidDmp();
csdDmp();
cout << F("\n寄存器值:") << uppercase << showbase;
cout << hex << ocr << dec << endl;
if (!mbrDmp())
{
return;
}
if (!sd.volumeBegin())
{
cout << F("\n卷初始化失败,内存卡是否格式化了?\n");
errorPrint();
return;
}
dmpVol();
}
3 SdFat 库内置错误类型
#include "SdFat.h"
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial)
{
yield();
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("代码,符号 - 错误操作"));
for (uint8_t code = 0; code <= SD_CARD_ERROR_UNKNOWN; code++)
{
Serial.print(code < 16 ? "0X0" : "0X");
Serial.print(code, HEX);
Serial.print(",");
printSdErrorSymbol(&Serial, code);
Serial.print(" - ");
printSdErrorText(&Serial, code);
Serial.println();
}
}
void loop()
{
}

4 查看文件信息
#include "SdFat.h"
// 1 FAT16/FAT32
// 2 exFAT
// 3 FAT16/FAT32 and exFAT
#define SD_FAT_TYPE 3
#if SD_FAT_TYPE == 0
SdFat sd;
File dir;
File file;
#elif SD_FAT_TYPE == 1
SdFat32 sd;
File32 dir;
File32 file;
#elif SD_FAT_TYPE == 2
SdExFat sd;
ExFile dir;
ExFile file;
#elif SD_FAT_TYPE == 3 // 同时支持 FAT16/FAT32/exFAT 文件系统的类
SdFs sd;
FsFile dir;
FsFile file;
#else
#error invalid SD_FAT_TYPE
#endif
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = 4; // CS 引脚
#define SD_CONFIG SdSpiConfig(SD_CS_PIN, DEDICATED_SPI, SD_SCK_MHZ(4)) // SPI 专用 4MHz
#define error(s) sd.errorHalt(&Serial, F(s))
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial)
{
yield();
}
Serial.println("输入任意字符开始");
while (!Serial.available())
{
yield();
}
// 初始化
if (!sd.begin(SD_CONFIG))
{
sd.initErrorHalt(&Serial);
}
// 打开根目录
if (!dir.open("/"))
{
error("根目录打开失败!");
}
// 打开根目录下的文件(遍历)
while (file.openNext(&dir, O_RDONLY))
{
file.printFileSize(&Serial); // 文件大小
Serial.write(' ');
file.printModifyDateTime(&Serial); // 文件修改时间
Serial.write(' ');
file.printName(&Serial); // 文件名
if (file.isDir()) // 如果是一个目录文件(文件夹),则在后面显示“/”
{
Serial.write('/');
}
Serial.println();
file.close(); // 关闭文件
}
if (dir.getError())
{
Serial.println("openNext 打开失败!");
} else {
Serial.println("完成!");
}
}
void loop()
{
}
5 文本文件读写
Arduino 使用 SD 卡模块(编辑中)